
All our research briefs are free to use but can not be reproduced for sale or placed behind a paywall or subscription based portal. The work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

Supporting roll-out of revised dengue prevention and control guidelines in Myanmar
Dengue prevention and control relies on the proficient application of guidelines by frontline health workers. This research brief outlines findings from our study that revealed major limitations to the use of participatory training to train health workers in Myanmar on revised dengue prevention and control guidelines. The approach did not result in better knowledge, skills or outbreak preparedness compared with more traditional didactic training.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Assessing antenatal care service delivery and uptake of key interventions in Ghana
All pregnant women in Ghana can receive antenatal care for free, reducing mortality and morbidity. Our study assessed the coverage of antenatal care services in 4 hospitals in the Ashanti region of Ghana and the quality of implementation of the services. Data was collected from December 2015 to May 2016.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Diabetes management for patients in rural Pakistan: initial findings
This research brief describes methods and findings from our study to deliver quality cardiovascular disease and diabetes care in rural healthcare facilities in Pakistan. The intervention includes screening overweight adults; standardised diagnosis; lifestyle education about diet, exercise and quitting smoking; standardised drug treatment for diabetes, hypertension and hyperlipidaemia; and active follow-up of patients.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Design and implementation of a non-communicable disease (NCD) screening programme in a rural African HIV clinic
One of the key strategies to reduce the global impact of NCDs is investment in the technology, processes and structures to identify, diagnose and treat these conditions as early as possible. This research brief describes our study to investigate the feasibility and outcomes of an integrated, affordable screening programme for risk factors associated with diabetes and hypertension in a busy HIV clinic in rural Swaziland.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Improving rational use of antibiotics in childhood upper respiratory tract infections in rural China – study methods, findings and implications
There are currently very few studies on antibiotic use in western, rural provinces of China where the inappropriate use of antibiotics may be greater due to a weaker health system. In our study, a comprehensive care package targeting both doctors and caregivers in township hospitals has reduced antibiotic prescribing in children with URTIs by more than half.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Cardiovascular disease risk reduction in rural China – interim findings and methods
Hypertension and diabetes are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD), but in rural areas of China, management is poor. Interim findings from our study show that our intervention package has improved medication adherence and promoted better lifestyle choices among patients in township hospitals across Zhejiang province.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Strengthening service delivery for malaria in pregnancy: an mHealth pilot intervention in West Nile, Uganda
Pregnant women are more susceptible to malaria than non-pregnant women. Our research shows that texting educational messages to health workers improves their knowledge about intermittent preventive treatment for malaria in pregnancy (IPTp) and increases IPTp coverage.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Assessing and addressing barriers to IPT2 uptake in Uganda
Intermittent preventive treatment in pregnancy (IPTp) is recommended by the World Health Organization as one of the 3 key strategies for the prevention and control of malaria in pregnancy. However, our study shows that various issues are hindering the effective provision of antenatal care and IPTp for women in Uganda. This policy brief summarises these obstacles and makes a number of key recommendations, including the development of a job aid for health workers and the introduction of computerised recording and reporting systems at health facilities.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Health reporting in The Kathmandu Post: 2013 – 2014
An infographic summarising findings from our analysis of 185 articles in The Kathmandu Post between 2013 and 2014. It shows the 7 main themes being reported and the relative frequency of stories within those categories. Issues about health service delivery, e.g. lack of equipment and staff, were written about most frequently, but overall we found that reporting focused on description rather than interrogation of health issues.
PDF Version | HTML Version
What health issues can Nepali journalists write about?
An infographic summarising the list of health issues that Nepali journalists said they could write about in their respective media outlets. Standards of performance and negligence of doctors and lack of adequate and free urban health services were among the key themes they identified.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Women and their mental and social wellbeing during multi-drug resistant TB treatment in Nepal
Treatment for multi-drug resistant TB is long and arduous and can cause depression and poor mental and physical health in patients. Our research sheds new light on the additional negative influence of gender and marital status on women’s mental and social wellbeing during their MDR-TB treatment.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Extended seasonal malaria chemoprevention: is it effective and acceptable in areas with longer rainy seasons in Ghana?
Extending seasonal malaria chemoprevention (SMC) from the usual 3 months to 5 months can significantly reduce the burden of malaria in areas with longer rainy seasons. This research brief summarises the key findings from our study in Ghana to investigate how effective a longer SMC programme is in protecting children aged under 5 and how acceptable the treatment regime is to caregivers, health workers and communities.
PDF Version | HTML Version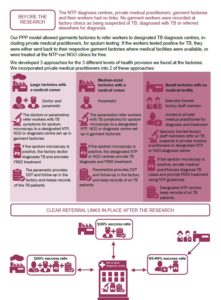
Improving access to TB care for garment factory workers using Public-Private Partnerships in Bangladesh
This brief outlines the challenges and impact of our research into providing garments factory workers with free TB treatment using Public Private Partnerships.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Schistosomiasis: Knowledge, attitudes and practices in Nampula province, Mozambique
A research brief infographic by our partners at Malaria Consortium exploring community perceptions and knowledge around schistosomiasis - a parasitic infection which mainly affects poor and marginalised communities.
PDF Version | HTML Version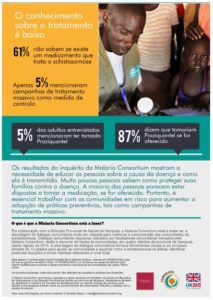
Schistosomiasis: Knowledge, attitudes and practices in Nampula province, Mozambique (Portuguese version)
A Portuguese language version of an infographic by our partners at Malaria Consortium exploring community perceptions and knowledge around schistosomiasis - a parasitic infection which mainly affects poor and marginalised communities.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Medical male circumcision: do women in Swaziland welcome it for their sons and at what age?
A research brief detailing our work in rural Swaziland to understand the attitudes, barriers and enablers among women to early infant male circumcision for their sons.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Structured 'pre-ART' care: a pathway to better health for people with HIV
This study, carried out in a hospital in rural Swaziland, shows how the introduction of structured pre-ART care can significantly improve the retention and management of patients with HIV.
PDF Version | HTML Version
Using behaviour change interventions to decrease tobacco use in Nepal
An overview of the findings from our behaviour change intervention that helped 37% of smokers to quit
PDF Version | HTML Version

